盒模型/媒体查询/em和rem的用法与区别
16lz
2022-04-12
盒模型/媒体查询/em和rem的用法与区别
1.盒模型
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>盒模型</title></head><style>html{margin: 0;padding: 0;font-size: 10px;}div{width: 20rem;height: 20rem;font-size: 2rem;background-color: red;/* 边框 */border: 1rem dashed blue;/* 内边距 */padding: 0.5rem 1rem 1.5rem;/* */background-clip: content-box;}.border-box{box-sizing: border-box;/* Total width: 200pxTotal height: 200pxContent box width: 200px -(2 * 10px) - (2 * 10px) = 160pxContent box height: 200px + (2 * 20px) - (1 * 5px) - (1 * 15px) = 160px */}.content-box{box-sizing: content-box;/* Total width: 200px +(2 * 10px) + (2 * 10px) = 240pxTotal height: 200px + (2 * 20px) + (1 * 5px) + (1 * 15px) = 240pxContent box width: 200pxContent box height: 200px */}</style><body><div class="border-box">border-box</div><br><div class="content-box">content-box</div></body></html>
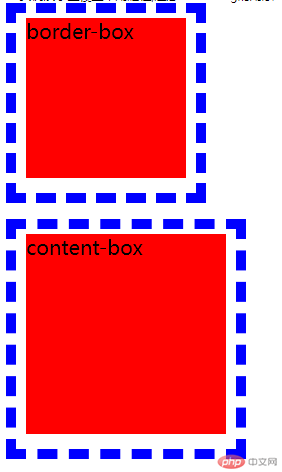
box-sizing的属性border-box会使总宽度不变,内容宽度==(总宽度-边框border-内边距padding);box-sizing的属性content-box会使内容宽度不变,总宽度==(内容宽度+边框border+内边距padding);*:box-sizing与外边距margin无关
2.媒体查询
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>媒体查询</title></head><style>div{background-color: brown;width: 100px;height: 100px;margin-bottom: 10px;color: #FFF;}@media (max-width: 400px) {div:first-of-type{background-color: red;}}@media (min-width: 401px) and (max-width: 600px) {div:nth-of-type(2n){background-color: yellowgreen;}}@media (min-width: 601px) {div:nth-of-type(3){background-color: lightseagreen;}}</style><body><div>媒体查询1</div><div>媒体查询2</div><div>媒体查询3</div></body></html>
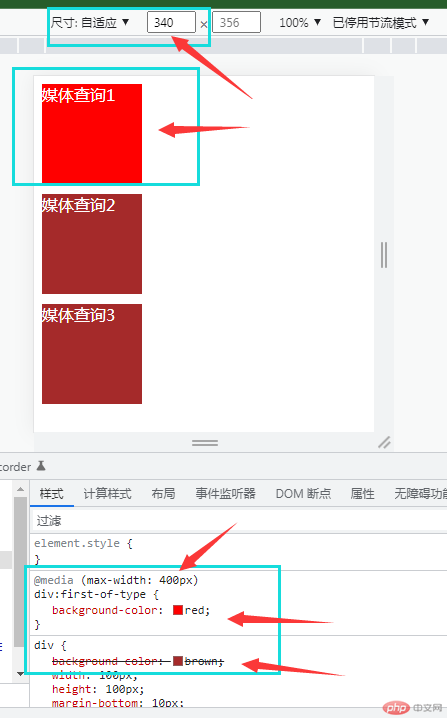
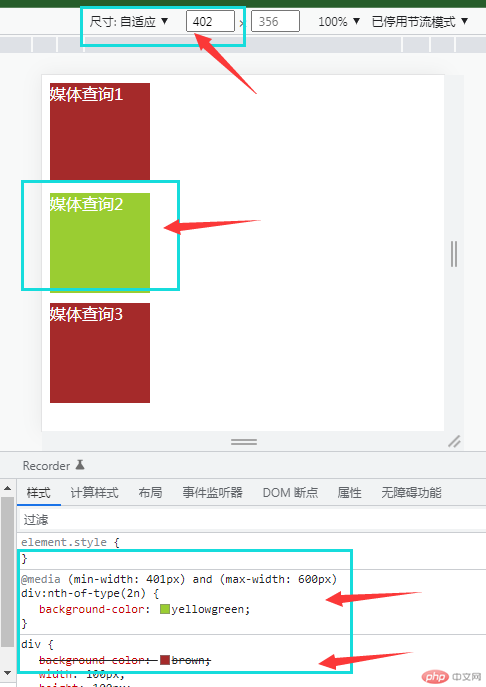
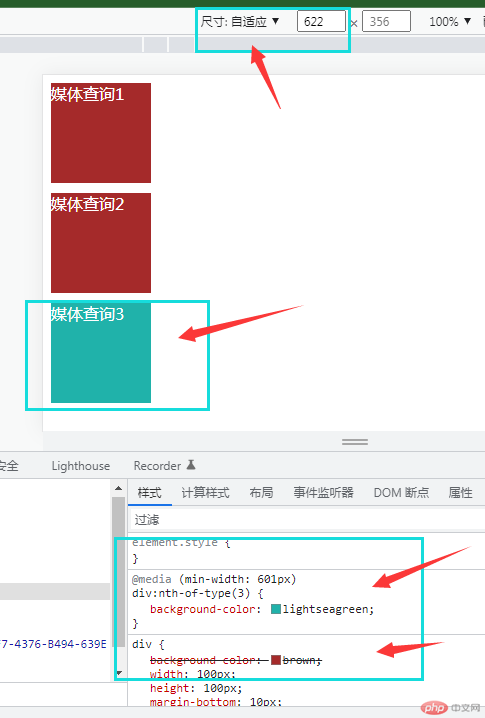
“媒体查询”主要通过
@media来判断当前viewport宽度,来对html进行调整
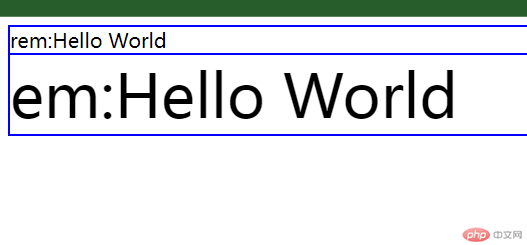
3. em和rem的用法与区别
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="zh-CN"><head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>em和rem的用法与区别</title></head><style>html{/* 设置根元素字体大小:10px */font-size: 10px;}div{border: 1px solid blue;}.box1{/* 设置父元素字体大小:20px */font-size: 20px;}.box2{/* 2rem = 2*根元素10px == 20px */font-size: 2rem;}.box3{/* 3em = 3*父元素20px == 60px */font-size: 3em;}</style><body><div class="box1"><div class="box2">rem:Hello World</div><div class="box3">em:Hello World</div></div></body></html>
1.
rem是相对于根元素进行计算;而em是相对于当前元素或父元素的字体大小,如果没有则根据根元素进行计算。(em计算优先级:当前元素>父元素>根元素)。
2.rem不仅可以设置字体的大小,还支持元素宽、高等属性。
3.em是相对于当前元素或父元素进行换算,层级越深,换算越复杂。而rem是相对于根元素计算,避免层级关系。
更多相关文章
- Android应用程序四大组件
- android的五大布局详解
- android投屏和媒体共享相关 && audio focus机制相关 && AudioTra
- JavaScript 字符串常用方法和数组api
- 字符串和数组常用API
- 表单、iframe后台、元素样式来源优先级
- Android五大布局(二)——RelativeLayout、TableLayout 和AbsoulteL
- Android(安卓)多媒体
- 一些关于RelativeLayout属性的用法
