C++成员函数中const的使用详解
目录
修饰入参
值传递
址传递
const修饰入参
修饰返回值
修饰函数
总结
const 在C++中是一个很重要的关键字,其不光可以用来修饰变量,还可以放在函数定义中,这里整理了其在函数中的三个用法。
修饰入参
首先我们要明白在C++中调用函数时存在两种方法,即传递值和传递引用。
值传递
值传递时,调用函数时会创建入参的拷贝,函数中的操作不会对原值进行修改,因此这种方式中不需要使用 const 来修饰入参,因为其只是对拷贝的临时对象进行操作。
址传递
传递地址时函数中的操作实际上是直接对原来的值进行修改,因此我们这里可以使用 const 修饰入参。
const修饰入参
当const修饰函数入参时表示该参数不能被修改,这个是最好理解的,比如一个函数的功能是拷贝,那么入参中的源文件都会用 const 修饰。void A::show(const int *b) { cout << "show const"; // error: read-only variable is not assignable // *b = 2; cout << b << endl;}
接下来我们要关注的是这里 const 对于函数重载的作用,这里给出结论,欢迎大家讨论,对应按值传递的函数来说 const 不会有重载的效果,但是传递指针和引用是会有重载的效果。void A::show(const int b)// void A::show(int b) // error class member cannot be redeclaredvoid display(int *num); // overloadvoid display(const int *num); // overloadvoid fun(A &a); // overloadvoid fun(const A &a); // overload
函数重载的关键是函数的参数列表——即函数特征标(function signature)。如果两个函数的参数数目和类型相同,并且参数的排列顺序也相同,则他们的特征标相同,而变量名是无关紧要的。
总结一下注意点:
如果输入参数采用“值传递”,由于函数将自动产生临时变量用于复制该参数,该输入参数本来就无需保护,所以不要加 const 修饰。例如不要将函数 void Func1(int x) 写成 void Func1(const int x)。
如果参数作为输出参数,不论它是什么数据类型,也不论它采用“指针传递”还是“引用传递”,都不能加 const 修饰,否则该参数将失去输出功能(因为有 const 修饰之后,不能改变他的值)。
如果参数作为输入参数,可以防止数据被改变,起到保护作用,增加程序的健壮性,建议是能加const尽量加上
上述测试代码如下:#include <iostream>using namespace std;class A {private: int a;public: A(int a) { this->a = a; } void show(int b); // error redeclared // void show(const int b); void display(int *num); // ok void display(const int *num); // ok void fun(A &a); void fun(const A &a); void happy(int * h); void hour(const int * h);};void A::show(int b) { cout << "show: " << b << endl;}void A::display(int *num) { cout << "display:" << *num << endl;}void A::display(const int *num) { cout << "const display:" << *num << endl;}void A::fun(A &obj) { cout << "fun: " << obj.a << endl;}void A::fun(const A &obj) { cout << "const fun: " << obj.a << endl;}void A::happy(int *h) { cout << "happy:" << *h << endl;}void A::hour(const int *h) { cout << "const hour:" << *h << endl;}int main() { A a(1); const A a2(11); int b1 = 2; const int b2 = 3; // test overload a.show(b1); a.show(b2); a.display(&b1); a.display(&b2); a.fun(a); a.fun(a2); // test const a.happy(&b1); // a.happy(&b2); // error cannot initialize a parameter of type 'int *' with an rvalue of type 'const int *' a.hour(&b1); a.hour(&b2); return 0;}// ouptutshow: 2show: 3display:2const display:3fun: 1const fun: 11happy:2const hour:2const hour:3
修饰返回值
const 修饰返回值时,表示返回值不能被修改。需要注意的是如果函数返回值采用“值传递方式”,由于函数会把返回值复制到外部临时的存储单元中,加 const 修饰没有任何价值。如果返回的是引用或指针,表示不能修改指向的数据。
一般用得多的是返回值是引用的函数, 可以肯定的是这个引用必然不是临时对象的引用, 因此一定是成员变量或者是函数参数, 所以在返回的时候为了避免其成为左值被修改,就需要加上const关键字来修饰。
我们可以看如下代码示例:#include <iostream>using namespace std;class Alice {private: int a;public: Alice(int a): a(a) {} int get_a() {return a;} const int* get_const_ptr() {return &a;} int* get_ptr() {return &a;}};int main() { Alice alice(1); int a1 = alice.get_a(); // ok cout << a1 << endl; const int a2 = alice.get_a(); // ok cout << a2 << endl; // error cannot initialize a variable of type 'int *' with an rvalue of type 'const int *' // int* b1 = alice.get_const_ptr(); const int* b2 = alice.get_const_ptr(); // ok cout << *b2 << endl; // ok // *b2 = 3; // error read-only variable is not assignable *(alice.get_ptr()) = 3; cout << alice.get_a() << endl; // 3 return 0;}
修饰函数
const 也可以用来放在函数末尾,用来修饰成员函数,表明其是一个常成员函数,这个对于初次接触C++的同学来说会有点陌生,不过这也是C++中严谨的地方。先看代码示例,学习任何编程技术都一定要写对应的代码,把它跑起来并分析结果才算是真正学会了,不会你只是知道了这个知识点,只知其然而不知其所以然。纸上得来终觉浅,绝知此事要躬行,这里的要躬行指的就是写代码。
首先来看如下的代码class Alice {private: int a;public: Alice(int a): a(a) {} void show();};void Alice::show() { cout << "hello Alice" << endl;}int main() { const Alice a(1); // error: 'this' argument to member function 'show' has type 'const Alice', but function is not marked const // a.show(); return 0;}
上述代码会报错,因为 show() 方法不是常成员函数,而 a 是常对象。本质上,成员函数中都有一个隐含的入参 this, 这个 this指的就是调用该方法的对象,而如果在函数的后面加上 const,那么这个 const 实际上修饰的就是这个 this。也就是说函数后加上了 const,表明这个函数不会改变调用者对象。
这里借用侯捷老师的图片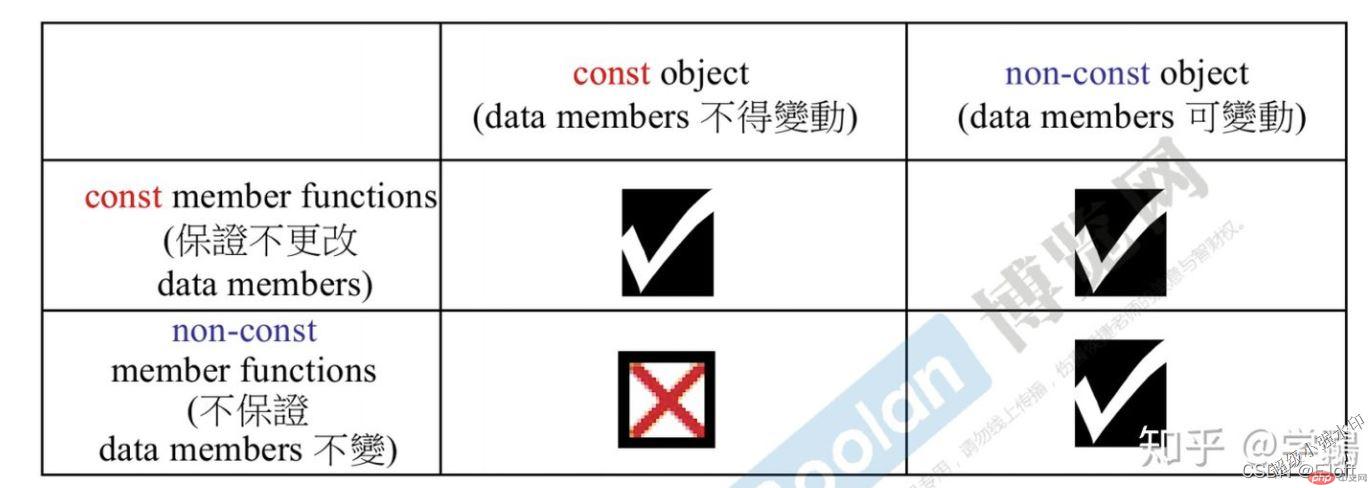
上面图片表明,在正常情况下:
non-const对象可以调用const 或者 non-const 成员函数
const 对象 只可以调用 const 成员函数
补充一点,如果成员函数同时具有 const 和 non-const 两个版本的话, const 对象只能调用const成员函数, non-const 对象只能调用 non-const 成员函数。如以下代码示例#include <iostream>using namespace std;class R {public: R(int r1, int r2) { a = r1; b = r2; } void print(); void print() const;private: int a; int b;};void R::print() { cout << "normal print" << endl; cout << a << ", " << b << endl;}void R::print() const { cout << "const print" << endl; cout << a << ", " << b << endl;}int main() { R a(5, 3); a.print(); const R b(6 ,6); b.print(); return 0;}// outputnormal print5, 3const print6, 6
这里也是建议能加 const 的时候就加。
更多相关文章
- Android平台开发-Power management-电源管理
- Android(安卓)两种方式优雅实现按钮防重复点击,防抖功能
- Android(安卓)加载图片文件 函数
- Android(安卓)cts测试命令
- JPA @Query时,无法使用limit函数的问题及解决
- 常用的前端JavaScript方法封装
- USB UMS MTP设置过程 (一)
- Android(安卓)Binder 机制详解
- Android(安卓)bluetooth介绍(三): 蓝牙扫描(scan)设备分析
